
News

How does a dynamic UPS work?
In “conditioning” mode, when grid power is available, the dynamic UPS stabilizes the voltage within pre-set tolerances. It provides power factor correction and protects the load from grid harmonics.
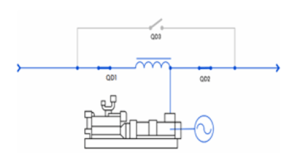
In “independent” mode, in the event of a grid power failure or voltage disturbances, the stored kinetic energy is recovered and transmitted to the synchronous machine, which acts as a generator.
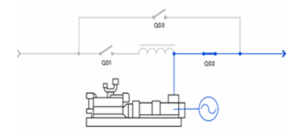
This happens seamlessly. Transfer to critical loads occurs within zero seconds. Following a power failure, the engine starts automatically. The electromagnetic clutch then engages, coupling the engine with the synchronous machine. The engine then supplies energy to the synchronous generator for an unlimited amount of time. The kinetic energy storage unit can be used to mechanically start the engine if the starter battery fails, thereby ensuring engine startup and providing an additional power source.
Advantages of UPS technology:
- Kinetic drive units provide dynamic, uninterrupted power using kinetic energy and are designed to meet the most demanding challenges in grid stabilization.
- Lower TCO, as drive units are more cost-effective for medium and high power ratings, reducing electricity consumption and maintenance costs.
- Smaller size. The number of components and monoblock structure make the dynamic UPS compact, reducing its size by up to 40% compared to a static UPS system with equivalent power capacity – making it the smallest on the market.
- Power conditioning. In addition to providing immediate emergency power, the dynamic UPS also functions as a power conditioner, filtering voltage spikes and harmonic disturbances while regulating load voltages within tolerance ranges to deliver clean energy to consumers
- Medium voltage systems, ideal for critical medium voltage loads or when covering larger distribution distances is required.
- Less environmental impact, as dynamic UPS systems do not require heavy batteries and do not generate chemical waste. Energy is immediately available from the kinetic energy storage unit to provide power until the diesel engine is activated.
